Electricity transmission in Finland - Prices & structure
The electricity transmission price is not subject to competition. However, the price of electricity transmission is always the same in the same destination, regardless of which electricity company you are a customer of. With the funds collected from electricity transmission, your electricity company covers the costs of its operations, such as maintenance of power lines and fault services.
Electricity transfer prices
The price of electricity transmission is a key factor in the Finnish consumer's electricity bill. You should always check the electricity contract for accurate and up-to-date prices.
| Year | High-rise apartment where electricity use is 2,000 kWh/year | Small house where electricity consumption is 20,000 kWh/year |
| 2016 | 7.83snt / kWh | 3.40snt / kWh |
| 2017 | 8.64snt / kWh | 3.71snt / kWh |
| 2018 | 9.35snt / kWh | 3.81snt / kWh |
| 2019 | 9.79snt / kWh | 3.98snt / kWh |
| 2020 | 10.02snt / kWh | 4.09snt / kWh |
| 2021 | 10.11snt / kWh | 4.30snt / kWh |
| 2022 | 9.96snt / kWh | 7.14snt / kWh |
| 2023 | 10.31snt / kWh | 7.34snt / kWh |
Electricity transfer basic fee
The basic fee for electricity transmission is a fixed fee that is billed to electricity consumers on a regular basis. It does not depend on the amount of electricity consumption, but is intended to cover the costs of maintaining and operating the electricity network. In your electricity bill, the normal electricity price, basic charges, transfer price and taxes are added together. The transmission of electricity cannot be tendered.
The basic fee is affected by:
- The area's infrastructure
- The transfer area's customer base
- Regional investments in the electricity network
Finland's electricity network
Finland, a sparsely populated country, is known for its challenging weather conditions and long distances.
Storms break the lines, and in winter the frosts can be harsh. These factors have naturally influenced the development of the country's energy network. Electricity transmission in Finland is flexible, diverse and efficient, meeting the needs of both industry and households. This is why predicting the price of electricity in Finland is relatively easy.
The energy network is designed to withstand various weather conditions and other challenges. The network has a wide selection of different forms of energy, such as nuclear power, hydropower, wind power, solar energy and fossil fuels.
In recent years, significant investments have been made in renewable forms of energy, especially wind and solar energy, in order to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote sustainable development.
Electricity Transmission in Finland
The history of Finland's energy network goes back to the beginning of the 20th century, when the first hydropower plants were built. These power plants were primarily for industrial use, but they also enabled the expansion of electrification to population centers.
This period was the time of industrialization for Finland, and electricity was an important promoting factor in it.
After the Second World War, Finland invested significantly in the development of its infrastructure, and the electricity network quickly expanded to different parts of the country. This period also meant a considerable increase in hydropower, and these turbines therefore formed the backbone of Finland's electricity production for a long time from the beginning.
☢️ In the 1960s nuclear power became part of Finland's energy supply. The Loviisa and Olkiluoto nuclear power plants began to produce a significant part of the country's electricity, and nuclear power was seen as an important way to reduce dependence on imported energy.
♻️ In the 1990s the era of reducing fossil fuels began in Finland. This was due to both the increase in environmental awareness and international agreements. At the same time, they started investing more in renewable forms of energy, such as wind and solar energy.
☀️ in the 2010s Finland's energy policy has focused even more on promoting renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency and increasing self-sufficiency.
However, the transition towards electric cars and the introduction of other electrified modes of transport places new demands on the electricity grid.
Today, Finland's energy network is a diverse and flexible system. In addition, the Finnish government and energy industry players have drawn attention to energy storage solutions, which enable a more consistent and reliable availability of electricity, and to the modernization and digitalization of the electricity network, which improve the efficiency and resilience of the network.
| Info | Estimate |
| 🛤️ The length of Finland's electricity network | 400 000 km |
| 🔌 Annual transmission losses of the main network | 1,5 % |
| ⚠️ Power outages | Approx. 100 h/year |
A map of Finland's electricity network
Finland's electricity network is a large and diverse system that covers the entire country, from southern cities to remote northern regions.
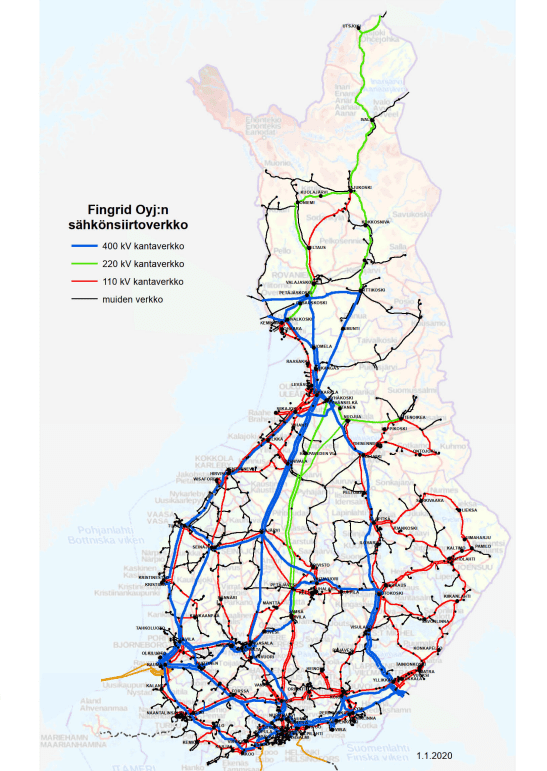
The map shows how electricity moves from production facilities to different parts of the country to distribution networks and finally to consumers. In particular, large transmission lines are prominently displayed, as are key hubs and connections to neighboring countries.
The structure of Finland's energy network
- Electrical network: Divided into high-voltage transmission network and regional distribution networks. The transmission network is managed by Fingrid and it connects the production facilities and the largest concentrations of electricity consumption.
- Gas network: Finland's gas infrastructure is smaller than many other European countries. The natural gas network serves Southern Finland in particular.
- Heat network: District heat production and distribution play a significant role, especially in urban areas.
The role of renewable energy
Wind power, solar energy and biomass have increased their share in the grid in recent years. With wind farms and solar energy projects, more and more green electricity is circulating in Finland's electricity grid.
Connections to neighbouring countries
The Finnish energy network is connected to the networks of neighboring countries, especially Sweden, Norway and Estonia. These connections enable the import and export of electricity, which increases the flexibility and stability of the system. Reliable electricity companies In Finland, they sell electricity imported from elsewhere to consumers.
Power grid disturbances
Disruptions in the electricity grid are situations where the distribution of electricity is interrupted temporarily or for a long time. These disturbances can be caused by, for example, storms, trees, freezing, technical faults or overloading:
- 🌪️ Storms and Natural Phenomenas: High winds, storms or freezing can knock down trees on power lines or damage them, leading to power outages.
- 🔧 Technical failure situations: Broken components or equipment failures can cause disturbances in the electrical network.
- ⚡ Overload: Sudden large power usage spikes can overload the network and lead to outages.
- 🔍 Prevention and repair: Electricity companies constantly monitor the network and try to anticipate, detect and repair faults as quickly as possible.
- 💰 Compensations: In certain situations, consumers have the right to receive compensation for long-term power outages from the electricity company.
FAQ
How much does electricity transfer cost?
The electricity transfer fee varies between different electricity companies and regions. It usually consists of a fixed basic fee and an energy fee determined according to consumption (cents/kWh). You can find out the exact price from your own electricity company, which invoices the transfer fee.
How is electricity transfer calculated?
The cost of electricity transmission is usually calculated as follows:
Transfer fee=(Basic fee)+(Energy fee*Consumed kWh).
Why can't electricity transmission be tendered?
Electricity transmission is by nature a natural monopoly, because it is economically and practically more efficient for one company to be responsible for the construction and maintenance of the electricity network in a certain area. That is why the state has given exclusive rights to certain companies to transmit electricity in certain areas. Instead, the sale of electricity itself can and should be tendered.





